Connect: a peek under the hood
Connect consists of visible and invisible parts.
The invisible parts process the Connect job to provide the actual output. This topic introduces you to those parts.
Here's a simplified, graphical representation of the architecture of PrintShop Mail Connect.
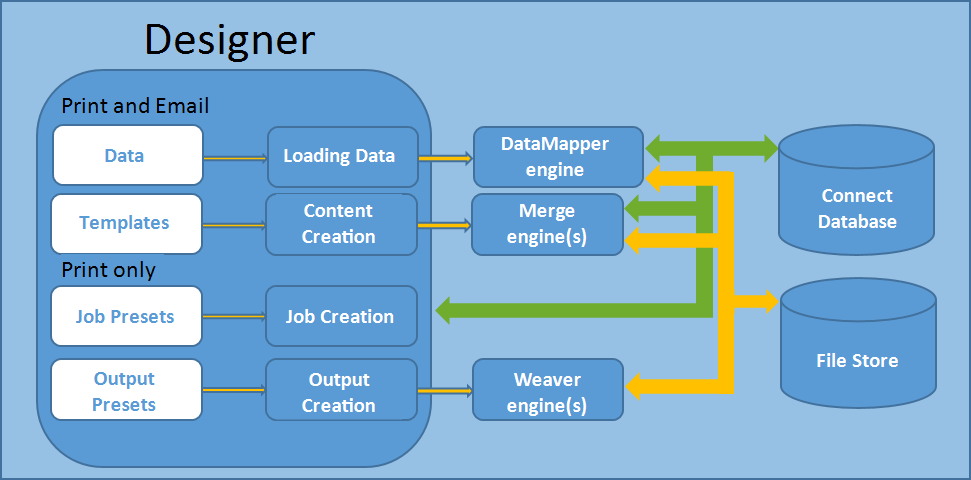
The Connect database
The Connect database is the database back-end used by Connect itself when processing jobs. It can be either the MySQL instance provided by the Connect installer, or a pre-existing (external) instance (see Database Considerations).
All generated items (records, content items etc.) are stored in this database .
Email content items are not stored in the Connect database.
A clean-up of the database is performed at regular intervals in accordance with the settings (see Clean-up Service preferences).
The File Store
Connect has its own File Store which it uses for transient files.
The Clean-up service takes care of removing obsolete files when those files are not marked as permanent (see Clean-up Service preferences).
The engines
DataMapper engine. A DataMapper engine extracts data from a data file.
Merge engine/s. A merge engine merges data with a template using the scripts in the template, in order to create (Print
The number of merge engines is configurable (see Merge engine scheduling): it can be increased depending on the capacity of the machine that runs the solution (see Performance Considerations).
Weaver engine . The Weaver engine create
The number of Weaver engines is configurable as well (see Weaver engine scheduling).
Speed units
The number of 'speed units' is the maximum number of Merge engines or Weaver engines that are allowed to work in parallel. The output speed of all engines together is limited to a certain number of output items (web pages, emails, or printed pages) per minute. How many speed units you have and what the maximum total output speed will be is determined by your licence and any additional Performance Packs you might have.
Each Merge engine and each Weaver engine needs at least one speed unit. However, since the number of engines is configurable, and since small, medium and large jobs may run concurrently, the number of engines in use may not match the number of available speed units. When there are more speed units than there are engines in use, the Connect server distributes the speed units and the maximum output speed to the engines proportionally.